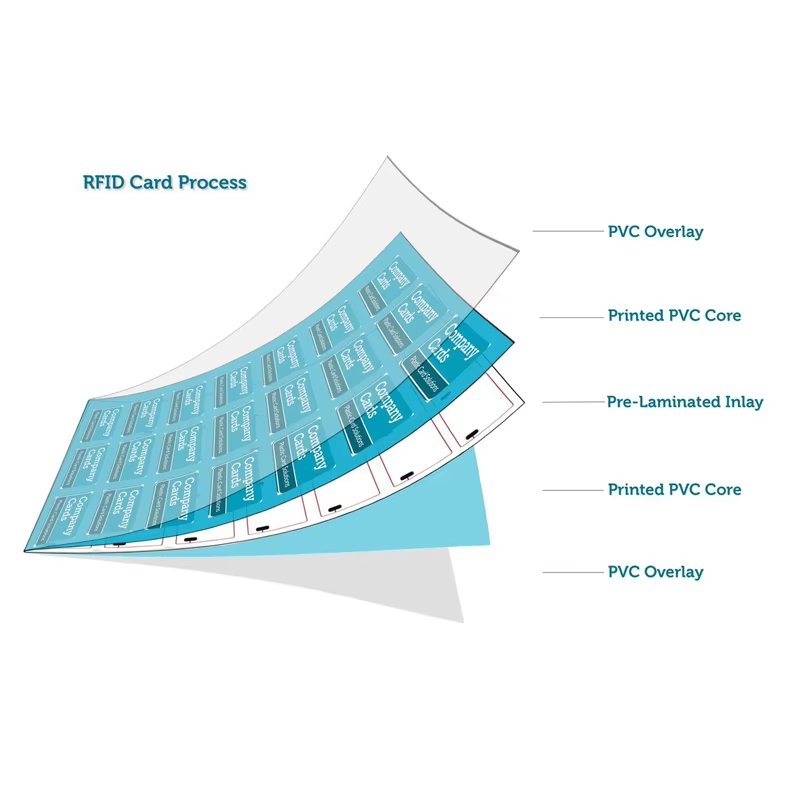
Smart Card Prelam Inlays: What You Need to Know
Uncover the secrets of smart card prelam inlays! Learn about their crucial role, manufacturing process, and applications. Find the right manufacturer for your needs!
Electronic tags (RFID tags) come in a variety of designs, shapes, sizes, and operating frequencies, all of which depend on the physical properties of the object to which the tag is attached and the specific application requirements. In the Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) system, electronic tags are widely used and come in various types, each differing in structure, appearance, and function.
When selecting a tag, multiple factors must be considered. The following guide sorts out the classification and characteristics of electronic tags from the perspectives of working mode, readability, operating frequency, packaging form, and more.
| Type | Has Own Power Supply | Working Characteristics | Scope of Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Active | ✅ | Actively sends data, long distance | Logistics, container management, etc. |
| Passive | ❌ | Relies on reader power supply, low cost | Retail, books, asset management, etc. |
| Semi-active | ✅ (powered only) | Relies on reader activation to backscatter data | Temperature and humidity monitoring, industrial equipment, etc. |
💡 Tips: Most of the RFID tags on the market are passive, because they do not require power, are small in size, low in cost, and offer great cost-effectiveness.
The information in the chip is written by the manufacturer and cannot be changed once written. Commonly used for identity recognition, anti-theft detection, etc.
The user writes data during initial use, and it cannot be changed afterward. Suitable for high data security scenarios.
These contain programmable memory (such as EEPROM), support repeated erasing, and are widely used for asset management, inventory tracking, etc.
Can record additional information such as temperature and pressure, ideal for cold chain logistics or environmental monitoring. Mostly active or semi-active.
Support direct communication with other devices, usually active, used for complex device data interaction.
Generally, the data capacity of RFID tags ranges between 64 bits and 2KB. The larger the tag capacity, the more information it can store and the longer it can function independently—but with increased cost.
| Capacity | Application Scope |
|---|---|
| 64–128 bit | Simple code identification |
| 512 bit | Can store basic product information |
| 1 KB+ | Independent use, no database required |
| Frequency Band | Frequency Range | Features | Application Scenarios |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low Frequency (LF) | 30–300 kHz | Strong penetration, short transmission distance | Animal identification, access control |
| High Frequency (HF) | 3–30 MHz (e.g., 13.56MHz) | Low cost, medium reading distance | Library, bus card |
| Ultra-High Frequency (UHF) | 860–960 MHz | Long reading distance, fast speed, susceptible to interference | Warehouse, logistics, supply chain |
| Microwave | 2.45GHz and above | Longer reading distance, high cost | Special environments |
| Project | Parameters |
|---|---|
| Size selection | 50×18mm, 80×27mm, 128×18mm and other options |
| Surface material | PET / Coated Paper / Thermal Paper |
| Chip type | M4D / M4E / M4QT / M5 / M6 / U8 / U9 |
| Memory capacity | 32 / 128 / 512 bits |
| Working frequency | 860–960MHz (UHF) |
| Protocol standard | EPC C1G2 / ISO18000-6C |
| Reading distance | Up to 6 meters (depending on the reader and environment) |
| Service life | 10 years, supports 100,000 reads and writes |
| Tag type | Dry inlay (no glue), Wet inlay (with glue) |
| Functional features | Waterproof / Weatherproof / Customizable appearance and printing |
| Packaging method | Roll packaging: 1000 sheets/roll, 2000 sheets/roll or OPP bag packaging |
| Application areas | Smart posters, electronic payment, logistics, warehousing, event management, asset tracking, etc. |
To solve the poor penetration issue of UHF tags, dual-frequency RFID tags are emerging, combining the strengths of low and high frequencies. These tags are activated by a low-frequency signal, then return data via a high-frequency signal. They offer both long-range reading and strong penetration, making them ideal for complex environments such as animal identification, sports timing, and metal interference.
When choosing RFID tags, you shouldn’t blindly pursue high performance or long range. Instead, evaluate based on the actual application scenario:
Do you need long-distance reading?
Or stronger penetration?
Do you need to write data repeatedly?
What material is the tag attached to?
All these factors must be taken into account.
🧠 Tips:
For warehouse management, UHF read-write tags are ideal.
For books or access control, HF read-only tags work best.
In cold chain logistics or animal management, active or dual-frequency sensor tags are often necessary.
Please contact us!
Newest trends and common knowledge in RFID laundry tags.

Uncover the secrets of smart card prelam inlays! Learn about their crucial role, manufacturing process, and applications. Find the right manufacturer for your needs!

Discover the Top 10 RFID Company shaping 2025! From retail to healthcare, these innovators are transforming industries.

Jinsha Ruins Museum utilizes UHF RFID tags for smart ticketing, visitor tracking, and personalized experiences, enhancing cultural communication and service.
Didn’t find what you want? Ask our manager for help!