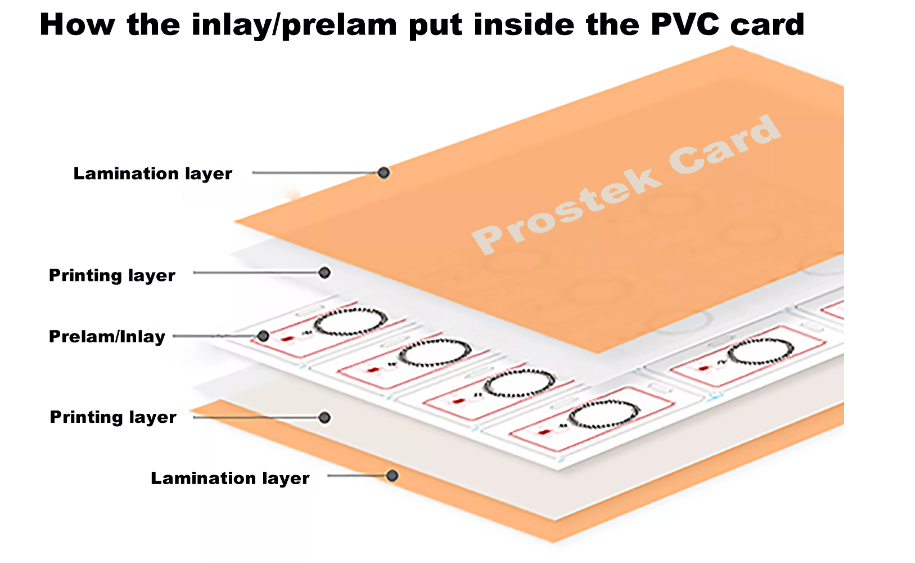
How RFID Card Prelam Inlays Improve Card Durability
RFID Card Prelam Inlays enhance card durability with advanced materials and engineering, ensuring long-lasting performance and reliability in various environments.
RFID Card protocol refers to a set of rules and standards followed when communicating between RFID cards and readers. Since there is no unified international standard, different manufacturers or applications choose different protocols. Currently common protocols include ISO10536, ISO14443, ISO15693, and ISO18000.
| Standard Name | Frequency Range | Application Scenarios |
|---|---|---|
| ISO14443 | 13.56 MHz | Access control, bus cards, campus cards, etc. |
| ISO15693 | 13.56 MHz | Library management, asset inventory |
| ISO10536 | 2.45 GHz | Long-distance identification in special environments |
| ISO18000 Series | Low to Ultra-High frequencies | Logistics tracking, supply-chain management, etc. |
Active Card
Built-in battery; longer read range (up to tens of meters), but higher cost, larger size, and limited lifespan.
Passive Card
Powered by the reader’s electromagnetic waves; small, low-cost, long lifespan; typical read range from a few centimeters to a few meters.
Low Frequency (LF)
125 kHz / 134.2 kHz: short-range, low-cost scenarios (e.g., animal identification, access control).
High Frequency (HF)
13.56 MHz: the most common band for libraries, bus cards, NFC, etc.
Ultra-High Frequency (UHF)
433 MHz / 915 MHz / 2.45 GHz: for logistics tracking, highway toll collection, etc., requiring longer read/write distances.
Inductive Coupling
Used in LF and HF cards; signal transmitted via magnetic-field coupling.
Backscatter Coupling
Used in UHF cards; card reflects the reader’s RF signal and modulates data onto it.
Read-Only Card
Data written at manufacture; users can only read.
Read-Write Card
Data can be written and modified multiple times.
CPU Card
Built-in microprocessor; supports more complex security applications.
Energy Transmission
The reader transmits RF signals; the card either converts these via its antenna into power (passive) or uses its own battery (active).
Data Communication
Passive Card: Uses modulation (backscatter) to superimpose data onto the reflected signal.
Active Card: Actively transmits its own RF signal back to the reader.
Protocol Process
Covers the physical layer (antenna design and power), initialization and anti-collision (to avoid multi-card interference), and the transmission protocol (data formats, encryption, etc.).
Selection: Choose the right frequency band and protocol for your application.
Integration: Ensure reader-card compatibility, reducing development and debugging time.
Security: Different protocols’ encryption and anti-collision features impact overall system security.
This article is organized around the RFID Card protocol to help beginners quickly master radio-frequency-card communication standards and principles. Welcome to share and comment!
If you need to know about the customized solutions, chip types or industry applications of RFID cards, please contact our professional team. We have more than 15 years of RFID production experience, support OEM customization services, and our products are exported to all over the world.
Newest trends and common knowledge in RFID laundry tags.

RFID Card Prelam Inlays enhance card durability with advanced materials and engineering, ensuring long-lasting performance and reliability in various environments.

Discover high-quality, customizable NFC Epoxy Tags for marketing, access control, and personal use. Elevate experiences with durable, innovative solutions!

Ucode 9 Tags enhance transportation efficiency with long-range tracking, durability, high memory capacity, and global compliance for real-time asset management.

As one of the top RFID Tag manufacturers in China, we specialize in high-quality RFID Tag and other RFID products designed to meet the diverse needs of various industries.
@ 2024 RFID Laundry Tag. All right reserved.
Didn’t find what you want? Ask our manager for help!